Nutrient Analysis Plus
Nutrient Analysis Plus
Optimal nutrient supply is crucial for health, energy, and well-being. The Nutrient Analysis Plus provides you with a comprehensive overview of your most important minerals, trace elements, and vitamins.
- Comprehensive analysis: Determination of essential minerals, trace elements, and vitamins for a well-founded assessment of your supply status.
- Early detection made easy: Detects deficiencies early before they noticeably affect your well-being and performance.
- Convenient & reliable: Easily take a blood sample at home, professional lab evaluation, and access clear results digitally.
So you don't have to guess what your body is missing.
In Stock
What values does this test measure?
What values does this test measure?
Further information on the values can be found here.
How does it work?
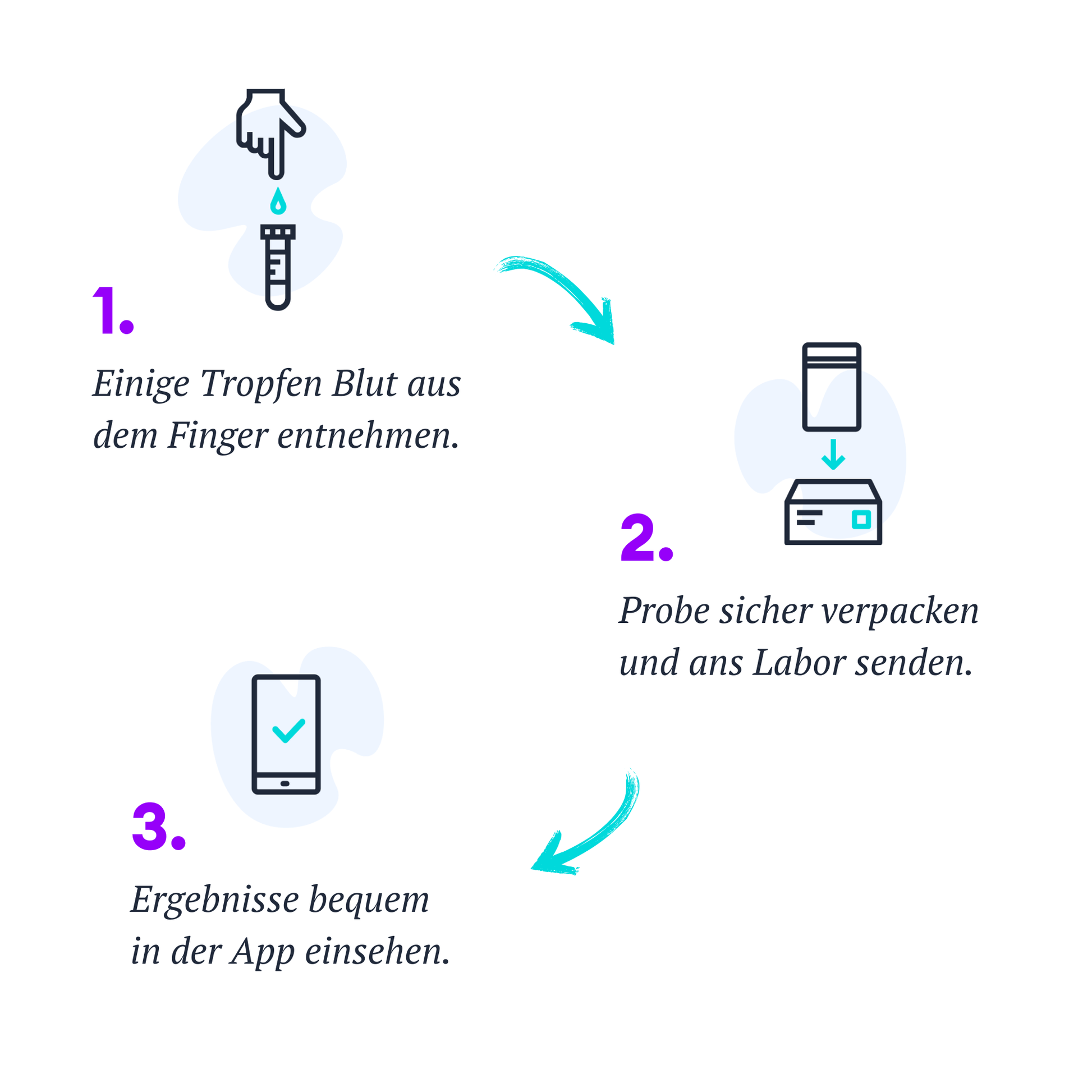
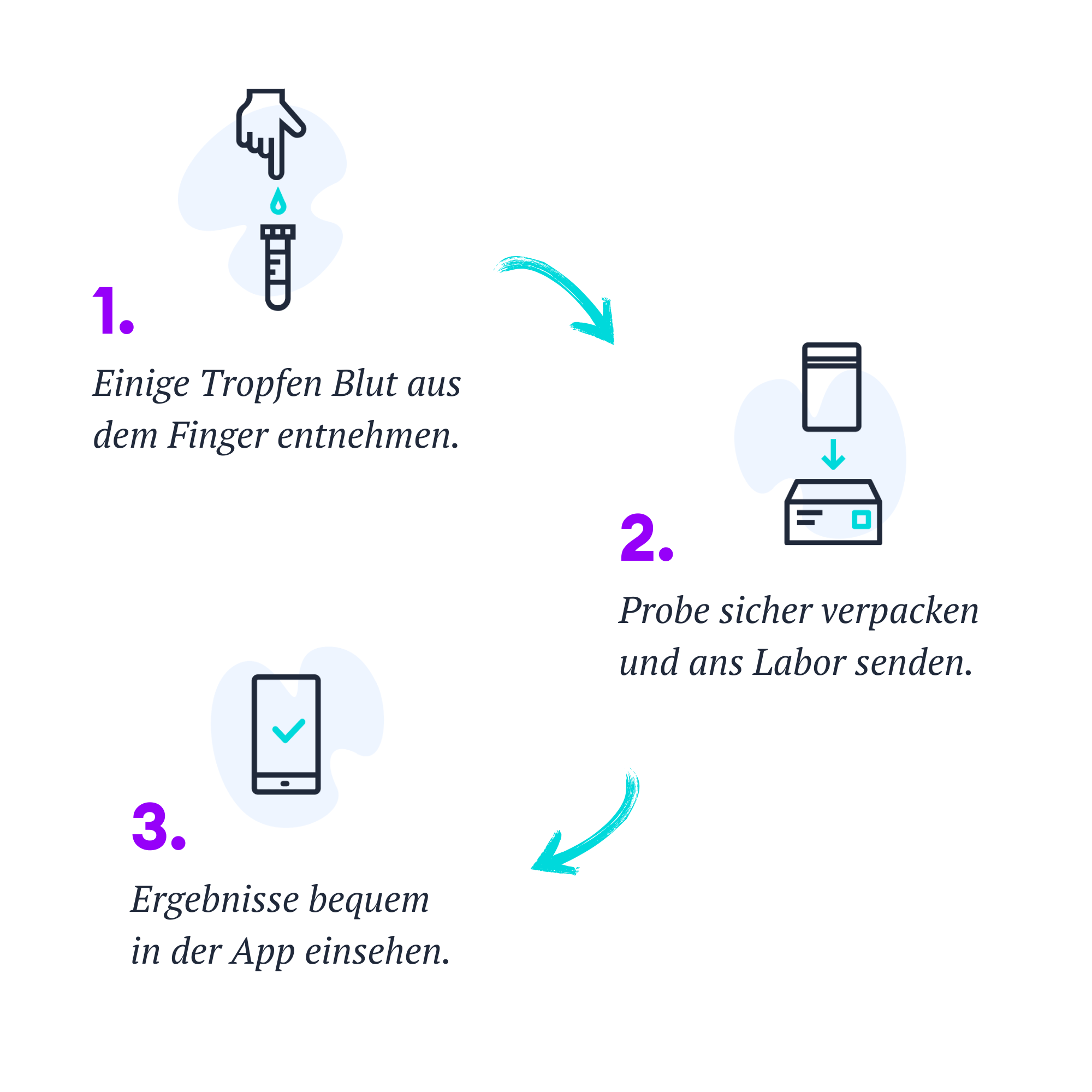
How does it work?
1. Take a sample with our test kit
2. Send the sample to the lab using the prepaid envelope
3. View results digitally after a few days
Why are the values reliable?
Why are the values reliable?
All tests offered by us are evaluated and validated in certified medical laboratories in Germany.
This is what the press says about our tests
Nutrient Analysis Plus: All details about the test
What benefits does this test offer me?
What benefits does this test offer me?
Our body needs vitamins, minerals, and trace elements to function optimally. Stress, unbalanced diet, or illnesses can lead to deficiencies – often unnoticed. The consequences: fatigue, concentration problems, weakened immune system, or muscle weakness.
With the Nutrient Analysis Plus, you get an overview of important vital substances such as Vitamin D, Vitamin B12 (including Holo-TC), folic acid, calcium, magnesium, iron (ferritin), zinc, selenium, copper, manganese as well as your lipid profile. This way, you can identify deficiencies early and take targeted action.
Why is this test important?
Nutrient deficiencies often develop gradually and negatively affect energy, immune system, skin, hair, muscles, and concentration. Especially athletes, vegans, or people under high stress benefit from regular monitoring.
How does the test work?
Simply take a blood sample at home, send it to the specialized laboratory, and receive a detailed report with clear explanations a few days later.
When is the test useful?
- Persistent fatigue or exhaustion
- Frequent infections or weakened immune system
- Hair loss, brittle nails, or dry skin
- Muscle weakness, cramps, or mood swings
Test nutrient levels now & Avoid deficiencies
The Nutrient Analysis Plus shows you whether your body is optimally supplied – and helps you to secure your health and performance in the long term.
What do the measured values mean?
What do the measured values mean?
25-OH vitamin D is the storage form of vitamin D that the body produces in the liver from vitamin D formed with sunlight or food. Vitamin D supports calcium absorption, ensures healthy bones and teeth, and plays an important role for muscles, nerves, and the immune system.
The 25-OH vitamin D test is the best method to check vitamin D status. Low levels can indicate too little sunlight, an unbalanced diet, or diseases and are associated with bone diseases such as osteoporosis or rickets. Excessive levels usually result from too high supplement doses and can strain the kidneys and liver.
Calcium
Calcium is an essential mineral primarily stored in bones and teeth. It ensures the stability of the skeleton and plays an important role in muscle function, blood clotting, and nerve signal transmission. A blood test measures the portion circulating in the blood.
Too low calcium levels can cause muscle cramps, tingling, or heart rhythm disturbances. Too high levels often indicate disorders of the parathyroid gland, certain tumors, or excessive intake of vitamin D.
Magnesium
Magnesium is an important biomarker for various diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and kidney problems. Measuring the magnesium level in the blood can help detect these diseases early and optimize treatment. A deficiency in magnesium can lead to muscle cramps, fatigue, and arrhythmias, while an excess is associated with kidney problems. Regular monitoring of magnesium levels is therefore essential for health.
Ferritin
Ferritin is a protein that stores iron in the body and releases it when needed. The ferritin level in the blood indicates how well the body's iron stores are filled and is therefore often used to assess iron status.
Low values usually indicate an iron deficiency or anemia. Elevated values may suggest inflammation, liver diseases, or iron overload.
Folic Acid
Folic acid in serum or plasma: The measurement of folic acid is used to determine the folic acid level in the blood. Folic acid is important for the formation of red blood cells and the smooth functioning of the nervous system. Deviations from the normal folic acid level can indicate various medical conditions, including anemia, pregnancy complications, or malnutrition.
Sodium
Sodium is an important mineral and electrolyte that regulates the body's water and salt balance. It also plays a central role in nerve signal transmission and muscle function. The body usually maintains sodium levels within a narrow range to keep essential functions stable.
Excessive levels (hypernatremia) often occur with fluid deficiency and can trigger thirst, confusion, or seizures. Low levels (hyponatremia) can result from significant fluid loss, kidney problems, or certain medications, leading to weakness, headaches, and, in extreme cases, consciousness disorders.
Transcobalamin
Transcobalamin is a protein that transports vitamin B12 in the blood and makes it available to the cells. A deficiency or dysfunction can lead to reduced vitamin B12 supply to the cells, which can cause various health problems.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is an essential vitamin required for the formation of red blood cells, the functioning of the nervous system, and the production of DNA. It is found almost exclusively in animal foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
A deficiency in Vitamin B12 can lead to anemia, fatigue, concentration problems, and nerve damage. Those at increased risk for a deficiency include primarily older people, vegetarians, vegans, or individuals with absorption disorders in the intestine.
HDL cholesterol
HDL cholesterol is often referred to as "good cholesterol" because it transports excess cholesterol from the vessels to the liver. There, it is broken down or recycled, reducing deposits in the arteries. Thus, HDL helps to keep the vessels healthy and free from calcifications.
High HDL levels are considered beneficial as they are associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases. On the other hand, low levels increase the risk of arteriosclerosis and heart attack.
LDL cholesterol
LDL cholesterol is referred to as "bad cholesterol" because it transports cholesterol from the liver to the body's cells. Excess LDL can deposit in the vessel walls and form so-called plaques. These deposits narrow the vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
High LDL levels are an important risk factor for arteriosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke. Low levels, on the other hand, are considered beneficial for vascular health.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are the main form of fats in the body and are primarily stored in fat cells. They are formed when excess energy from food is converted into fat. Some triglycerides circulate in the blood and serve as an energy source.
Elevated triglyceride levels can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, especially when LDL is high and HDL is low at the same time. Very high levels can also trigger inflammation of the pancreas.
Selen
Selenium is an essential trace element that is indispensable for the function of numerous enzymes, particularly antioxidant enzyme systems such as glutathione peroxidase. It supports the defense against cell damage caused by free radicals and plays a key role in thyroid function, especially in the conversion of thyroxine (T4) into the active triiodothyronine (T3).
A selenium deficiency can contribute to increased susceptibility to infections, thyroid dysfunction, muscle weakness, and cardiovascular diseases. A low selenium level is also observed in inflammatory diseases and autoimmune disorders.
Mangan
Manganese is a trace element that is necessary in small amounts for a variety of biological functions. It supports the activity of several enzymes important for energy metabolism, bone health, wound healing, and protection against oxidative stress. Manganese is also involved in the formation of connective tissue and the regulation of blood sugar.
A deficiency is rare but can lead to growth disorders, impairments in fat and carbohydrate metabolism, as well as neurological symptoms.
An excess is also possible and can have toxic effects, particularly on the nervous system.
Copper
Copper is an essential trace element required for numerous physiological processes such as the formation of red blood cells, the function of enzymes (e.g., superoxide dismutase), and energy production in cells. Copper also supports the development of the nervous system, iron utilization, and the strengthening of the immune system.
A deficiency can lead to anemia, increased susceptibility to infections, neurological symptoms, and connective tissue weaknesses. Conversely, elevated copper levels can occur, for example, in chronic inflammations or liver diseases.
Zinc
Zinc is an essential trace element involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions. It is crucial for the functioning of the immune system, cell division and regeneration, wound healing, and antioxidant protection. Zinc also influences hormone balance and skin health.
A zinc deficiency can lead to susceptibility to infections, delayed wound healing, hair loss, skin diseases, taste disorders, and even growth delays. In stressful situations, chronic illnesses, or with an unbalanced diet, the need for zinc may also increase.
Why is this test important?
Why is this test important?
Many nutrient deficiencies go unnoticed for a long time, but they can trigger fatigue, concentration problems, immune weakness, or muscle weakness. With the Nutrient Analysis Plus, you can check your most important vital substances and ensure that your body is optimally supplied.
When should I take this test?
When should I take this test?
- html
- In case of tiredness, exhaustion, or concentration problems.
- If you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet.
- If you regularly exercise and want to optimize your nutrient supply.
- In case of frequent infections or a weakened immune system.
- If you want to rule out a possible nutrient deficiency.
The Nutrient Analysis Plus helps you to detect deficiencies early, improve your supply specifically, and stay healthy in the long term.
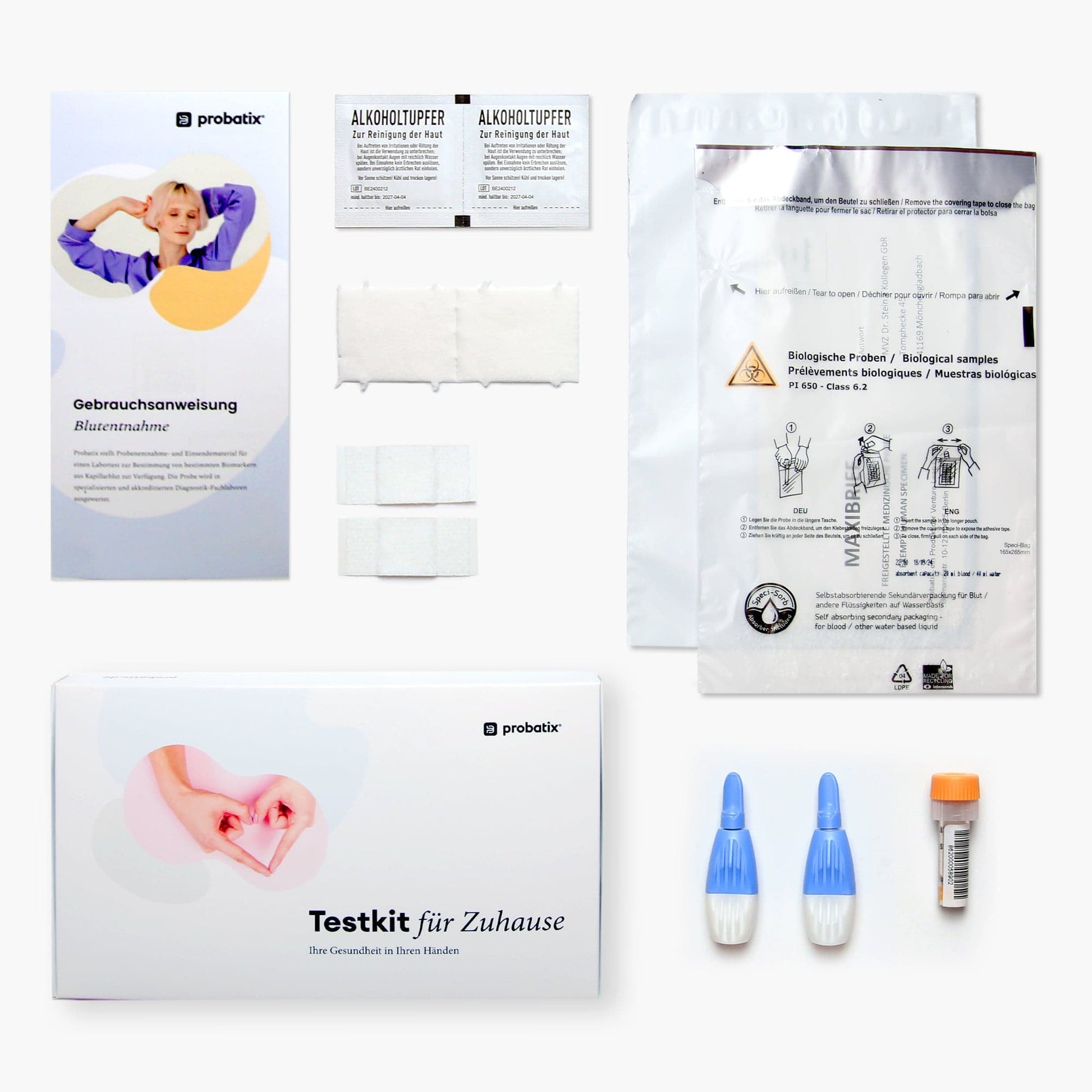
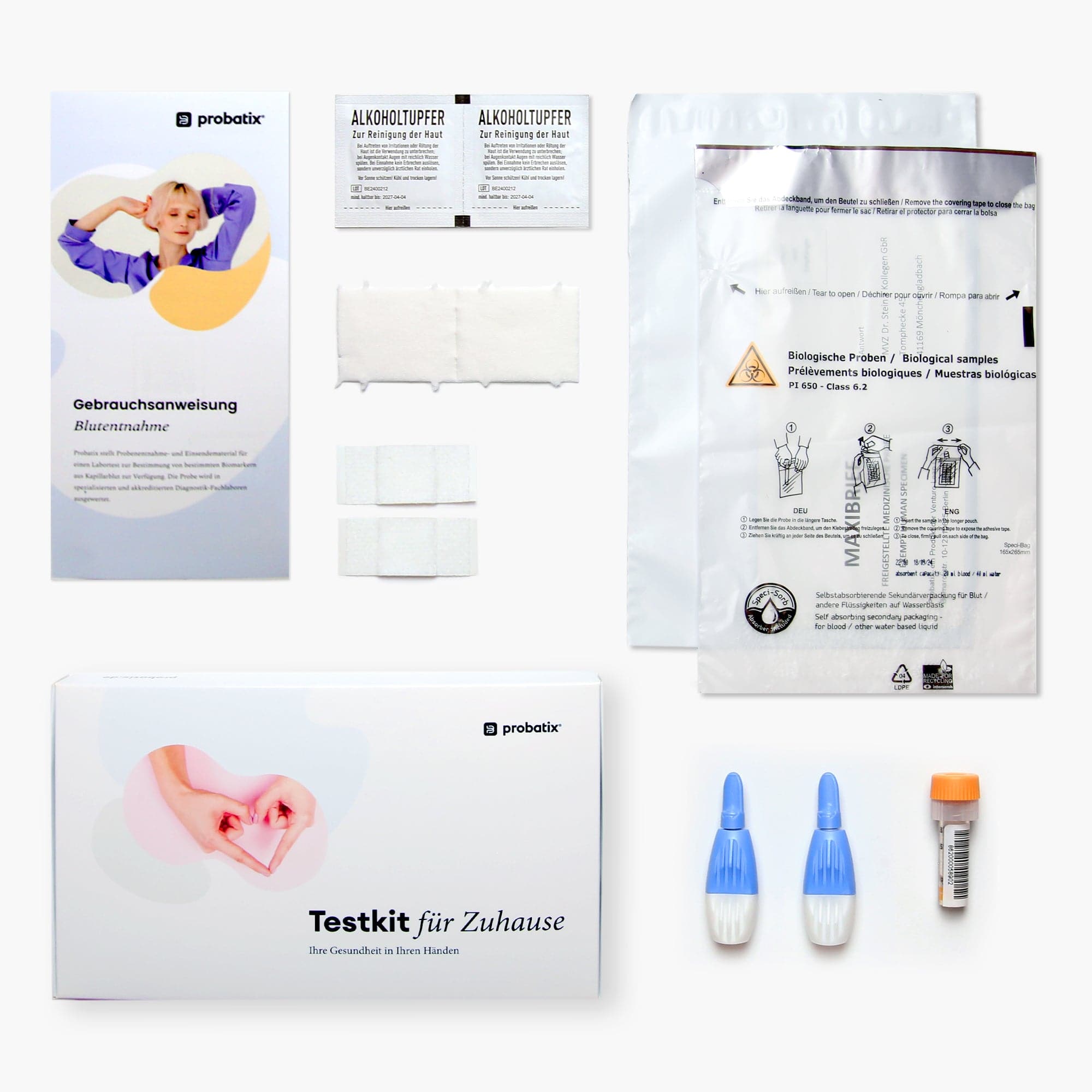
What is included in the test kit?
What is included in the test kit?
Where can I find the instructions?
Where can I find the instructions?
Bei Fragen hilft Ihnen auch immer gerne unser wunderbarer Support weiter: support@probatix.de
FAQ - More Frequently Asked Questions about the Test
FAQ - More Frequently Asked Questions about the Test
What is examined in the Nutrient Analysis Plus?
The Nutrient Analysis Plus measures essential vitamins, minerals, and trace elements: Calcium, Magnesium, Ferritin, Folic Acid, Sodium, Holo-TC, Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, LDL and HDL Cholesterol, Triglycerides, Zinc, Selenium, Copper and Manganese.
Who is this test suitable for?
The test is ideal for individuals who want to check their nutrient supply – especially with special diets, persistent fatigue, or nonspecific complaints.
How does the sampling work?
The sampling is simple and painless via capillary blood from the fingertip. You will receive a test kit with clear instructions for easy home use.
How long does it take to receive my results?
After submitting the sample, you will typically receive your lab results digitally within 3–5 business days.
Why are trace elements like zinc, selenium, and copper important?
Zinc supports the immune system and wound healing. Selenium has antioxidant properties and protects cells. Copper is essential for blood formation and energy metabolism.
What role do Vitamin B12 and Holo-TC play?
Vitamin B12 is crucial for nerve function, cell division, and energy production. Holo-TC is the active form of Vitamin B12 and a particularly sensitive marker for an emerging deficiency.
Why are calcium and magnesium measured?
Calcium is important for bones, muscles, and nerves.Magnesium supports muscle and nerve function and helps reduce stress. Both are essential minerals for energy and stability.
What happens if my values are outside the reference range?
If deviations are detected, you should discuss the results with a doctor. They can initiate further investigations or recommend targeted measures.
Das sagen unsere Kunden
Your benefits for your health
Test with minimal effort
Understanding Your Own Health
Recognize changes early