Cardiovascular Risk Profile
Cardiovascular Risk Profile
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death in Germany – often with preventable risk factors. The cardiovascular risk profile helps to check key blood values early that are associated with heart attack, arteriosclerosis, and high blood pressure.
- Relevant markers in focus: Measures apolipoprotein A1, apolipoprotein B, calcium, total cholesterol, HDL and LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, lipoprotein(a), sodium, and CRP (C-reactive protein) – a comprehensive range of risk parameters.
- Individual risk assessment: Provides insights into silent processes such as chronic inflammation, lipid metabolism disorders, or electrolyte imbalances.
- Simple & professionally evaluated: Blood sampling conveniently at home, professional analysis in a medical laboratory.
Know where you stand – with the Probatix cardiovascular risk profile.
In Stock
What values does this test measure?
What values does this test measure?
Further information on the values can be found here.
How does it work?
How does it work?
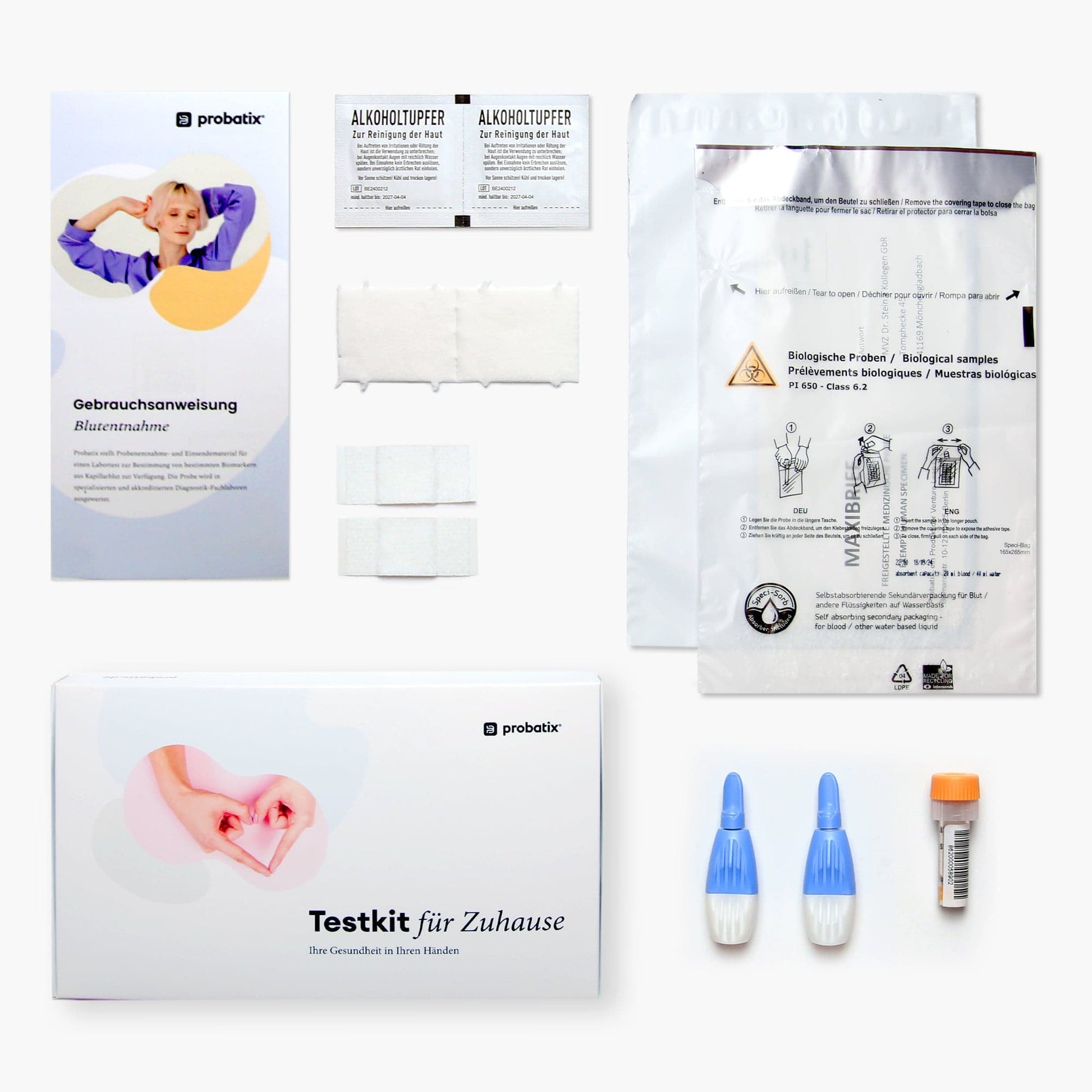
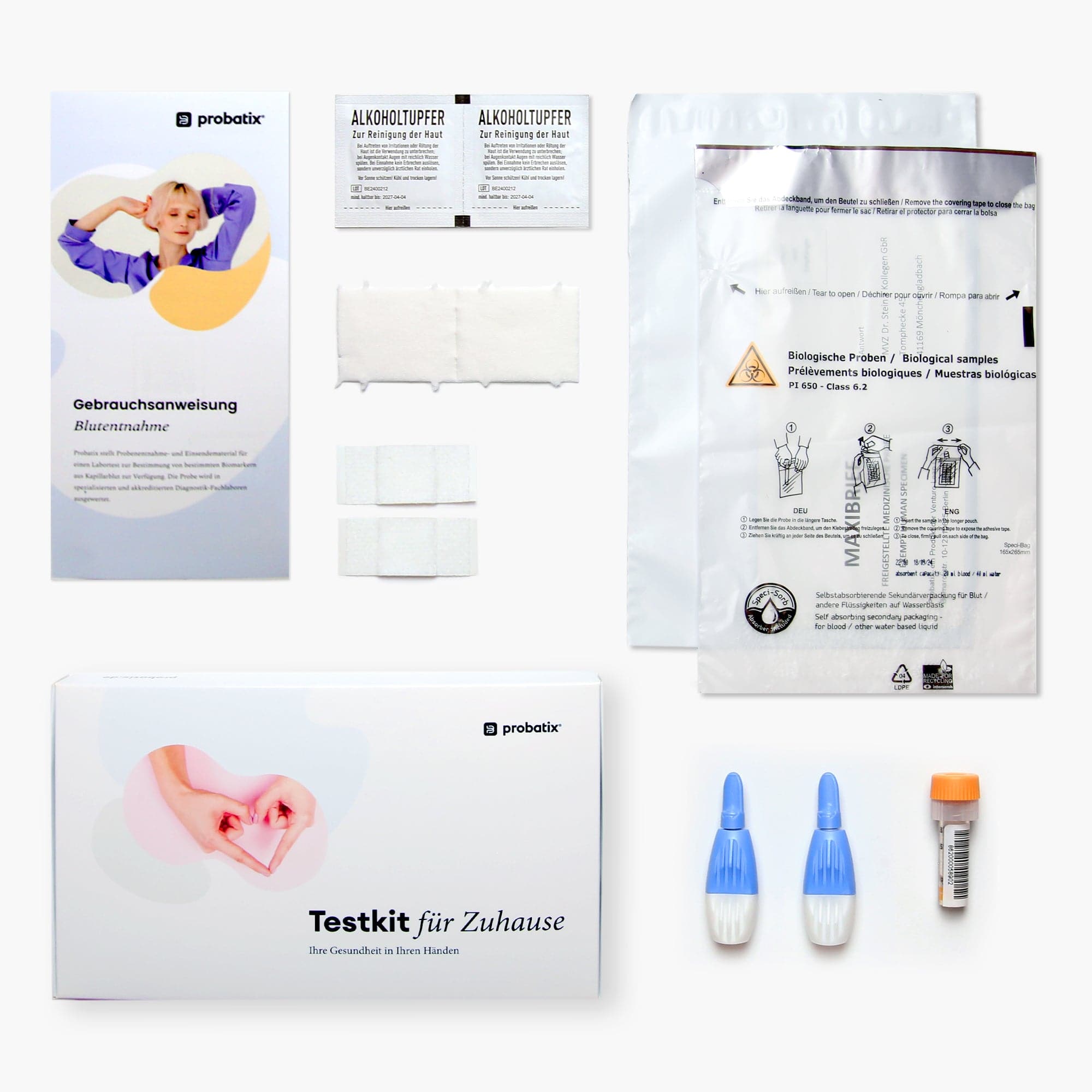
1. Take a sample with our test kit
2. Send the sample to the lab using the prepaid envelope
3. View results digitally after a few days
Why are the values reliable?
Why are the values reliable?
All tests offered by us are evaluated and validated in certified medical laboratories in Germany.
This is what the press says about our tests
Cardiovascular Risk Profile: All details about the test
What benefits does this test offer me?
What benefits does this test offer me?
Your heart works around the clock – and yet many risk factors for cardiovascular diseases remain unnoticed for a long time. Cholesterol levels, inflammation markers, and electrolytes can provide valuable insights into your heart health and help identify risks early. With the Cardiovascular Risk Profile, you receive a comprehensive analysis of key markers for your heart and vessels.
The test measures the following values:
- Apolipoprotein A1: A component of "good" HDL cholesterol, important for the reverse transport of cholesterol from the vessels.
- Apolipoprotein B: A central component of "bad" LDL cholesterol, which can promote deposits in the vessels.
- Total cholesterol: An important overall value that provides information about the lipid metabolism status.
- LDL cholesterol: The "bad" cholesterol that can deposit in the vessels and promote arteriosclerosis.
- HDL cholesterol: The "good" cholesterol that transports excess cholesterol from the blood.
- Triglycerides: An energy source, elevated levels of which increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)): A hereditary risk factor for heart attack and stroke. Elevated levels additionally strain the vessels.
- C-reactive protein (CRP): An inflammation marker that provides indications of chronic inflammation and vascular changes.
- Sodium: A vital electrolyte that regulates fluid and blood pressure balance.
- Calcium: Involved in muscle and nerve function, including the heart muscle.
Why is this test important?
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death in Germany. Risk factors often develop insidiously, without those affected noticing anything. An early review of the relevant values allows for timely preventive measures to be taken and personal risk to be reduced.
How does the test work?
The procedure is simple: With the supplied test kit, you take a small blood sample from your fingertip and send it to our certified specialist laboratory. You will receive your results digitally within a few days – including easy-to-understand explanations.
Symptoms for which you should take the test
The cardiovascular risk profile is particularly useful if you notice one or more of the following symptoms:
- High blood pressure or sudden blood pressure fluctuations
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing even with slight exertion
- Fatigue, exhaustion, or lack of energy
- Pressure or pain in the chest
- Dizziness or frequent headaches
- Tingling or numbness in arms and legs
- Family history of heart attack or stroke
- Overweight, diabetes, or elevated blood lipid levels
Identify cardiovascular risks early now
Stay informed and regularly check your key heart markers.The cardiovascular risk profile helps you identify potential risks in a timely manner and protect your heart health in the long term.
What do the measured values mean?
What do the measured values mean?
Cholesterol is a fat-like substance that the body needs for many important functions. It is a building block of cell membranes, a precursor for hormones such as estrogen and testosterone, and for the formation of bile acids. A portion is absorbed through food, but the majority is produced in the liver.
Too high cholesterol levels can lead to deposits in the vessel walls and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. However, a balanced level is important, as cholesterol is also indispensable for health.
LDL cholesterol
LDL cholesterol is referred to as "bad cholesterol" because it transports cholesterol from the liver to the body's cells. Excess LDL can deposit in the vessel walls and form so-called plaques. These deposits narrow the vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
High LDL levels are an important risk factor for arteriosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke. Low levels, on the other hand, are considered beneficial for vascular health.
HDL cholesterol
HDL cholesterol is often referred to as "good cholesterol" because it transports excess cholesterol from the vessels to the liver. There, it is broken down or recycled, reducing deposits in the arteries. Thus, HDL helps to keep the vessels healthy and free from calcifications.
High HDL levels are considered beneficial as they are associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases. On the other hand, low levels increase the risk of arteriosclerosis and heart attack.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are the main form of fats in the body and are primarily stored in fat cells. They are formed when excess energy from food is converted into fat. Some triglycerides circulate in the blood and serve as an energy source.
Elevated triglyceride levels can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, especially when LDL is high and HDL is low at the same time. Very high levels can also trigger inflammation of the pancreas.
Lipoprotein(a)
Lipoprotein (a), abbreviated as Lp(a), is a special form of LDL cholesterol. It consists of an LDL particle that additionally carries a protein called apolipoprotein(a). The level of Lp(a) is largely determined genetically and can hardly be influenced by diet or exercise.
Elevated Lp(a) levels promote the formation of deposits in the vessels, inflammation, and blood clots. Therefore, Lp(a) is considered an independent risk factor for heart attack and stroke – even if other cholesterol levels are normal.
C-reactive protein (CRP)
CRP (C-reactive protein) is a protein that the liver produces in response to inflammation. The level in the blood rises quickly when infections, tissue damage, or other inflammatory processes occur in the body. Therefore, CRP is often used as a general marker of inflammation.
A significantly elevated CRP level usually indicates an acute infection, while slightly elevated levels can also occur in chronic diseases. Normal values generally rule out a relevant inflammation.
Sodium
Sodium is an important mineral and electrolyte that regulates the body's water and salt balance. It also plays a central role in nerve signal transmission and muscle function. The body usually maintains sodium levels within a narrow range to keep essential functions stable.
Excessive levels (hypernatremia) often occur with fluid deficiency and can trigger thirst, confusion, or seizures. Low levels (hyponatremia) can result from significant fluid loss, kidney problems, or certain medications, leading to weakness, headaches, and, in extreme cases, consciousness disorders.
Calcium
Calcium is an essential mineral primarily stored in bones and teeth. It ensures the stability of the skeleton and plays an important role in muscle function, blood clotting, and nerve signal transmission. A blood test measures the portion circulating in the blood.
Too low calcium levels can cause muscle cramps, tingling, or heart rhythm disturbances. Too high levels often indicate disorders of the parathyroid gland, certain tumors, or excessive intake of vitamin D.
Apolipoprotein A1
Apolipoprotein A1 (Apo A-I) is the main protein of the "good" HDL cholesterol. It supports the transport of excess cholesterol from the vessels to the liver, where it is broken down and excreted. Thus, Apo A-I plays a central role in protecting the vessels from calcification.
High Apo A-I levels are associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases. Low levels, on the other hand, can be an indication of an increased risk of arteriosclerosis, especially if the "bad" LDL cholesterol is also elevated.
Apolipoprotein B
Apolipoprotein B (Apo B) is the most important transport protein of the "bad" cholesterol particles such as LDL and VLDL. Since each LDL particle carries exactly one Apo B, the Apo B value directly indicates how many atherogenic particles are circulating in the blood. Thus, it is a very significant marker for the risk of vascular calcifications.
A high Apo B value means an increased risk of heart attack or stroke. Low values, on the other hand, are considered favorable and indicate that fewer harmful particles are present in the blood.
Why is this test important?
Why is this test important?
Cardiovascular diseases are among the most common causes of death worldwide. Many risk factors – such as elevated cholesterol levels, silent inflammations, or unbalanced electrolyte levels – often go unnoticed for a long time. With the Cardiovascular Risk Profile, you can identify these factors early and take timely countermeasures.
When should I take this test?
When should I take this test?
- html
- In case of family history of cardiovascular diseases.
- If you suffer from high blood pressure, overweight, or diabetes.
- In case of recurring chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness.
- If you often feel tired, exhausted, or lacking energy.
- If you want to regularly check your cholesterol levels, inflammation markers, and electrolytes.
An early cardiovascular risk profile can help identify potential dangers in time and take active countermeasures.
What is included in the test kit?
What is included in the test kit?
Where can I find the instructions?
Where can I find the instructions?
Bei Fragen hilft Ihnen auch immer gerne unser wunderbarer Support weiter: support@probatix.de
FAQ - More Frequently Asked Questions about the Test
FAQ - More Frequently Asked Questions about the Test
What is examined in the cardiovascular risk profile?
The test measures key markers for cardiovascular health, including apolipoprotein A1, apolipoprotein B, total cholesterol, LDL and HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)], CRP (C-reactive protein), sodium and calcium.
Who is this test suitable for?
The cardiovascular risk profile is ideal for anyone who wants to assess their individual risk – especially with a family history, high blood pressure, overweight, diabetes, or lack of exercise.
How does the sampling work?
The sampling is done easily via capillary blood from the fingertip. You will receive a test kit with clear instructions, allowing you to conveniently perform it from home.
How long does it take to receive my results?
After sending the sample to our specialized laboratory, your results are usually available digitally within 3–5 business days.
What do cholesterol levels say about my cardiovascular risk?
LDL cholesterol is considered "bad cholesterol" because it can promote deposits in the vessels. HDL cholesterol, on the other hand, helps to transport excess cholesterol away. A balanced lipid profile is crucial for heart health.
What is Lp(a) and why is it important?
Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is a genetically determined risk factor. Elevated levels can significantly increase the risk of arteriosclerosis, heart attack, or stroke, even if other cholesterol levels are within the normal range.
Why is CRP measured?
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a marker of inflammation. Elevated levels indicate silent inflammations in the body, which can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
What happens if my values are outside the reference range?
If abnormalities are detected, you should discuss the results with a doctor. This allows for further examinations and individual measures for risk reduction to be initiated.
Das sagen unsere Kunden
Your benefits for your health
Test with minimal effort
Understanding Your Own Health
Recognize changes early